

For instance a case of influenza in a normal household setting does not require strict precautions, where as one in a long term care home might.

Precautions will vary according to the microorganism involved and the context of the case. (See Table) If the mode of transmission is known, precautions can be put in place to prevent outbreaks. There are six common modes of transmission of infection. Wear gloves, mask, and apron when needed.īy doing these things, you may stop an infection either to you or your care. Keep clothing clean by holding things away from you.
Insertion and maintenance of invasive devices are guided by published evidenced-based recommendations supporting education, training, and standardized care for patients with central lines, surgical sites, ventilators, and urinary catheters.

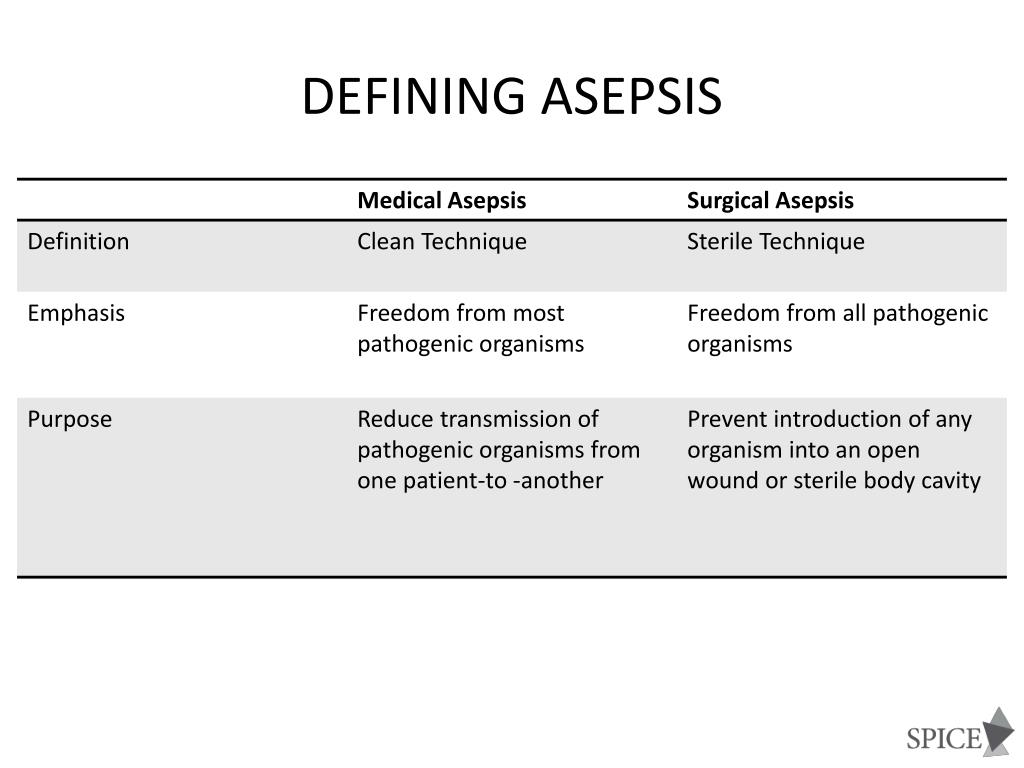
You do not have permission to view this object. A Compendium of Strategies to Prevent Healthcare-Associated Infections in Acute Care Hospitals. Clean technique leads to a decrease of the overall number of microorganisms present rather than the absence of microorganisms as is found in surgical asepsis.Ref 30-3 Yokoe DS, Mermel LA, Anderson DJ, et al. Clean technique, or medical asepsis, is another practice to prevent or reduce the risk of transmission of organisms from one person to another or from one place to another. Situations in which surgical asepsis technique is applied include surgery as well as other areas where invasive procedures are done such as placement of intravenous lines, urinary catheters, chest tubes, and any other indwelling devices. You do not have permission to view this object.Īseptic techniques, defined as the process for keeping away disease-producing microorganisms, may be used in any clinical setting. Guideline for hand hygiene in health-care settings: Recommendations of the Healthcare Infectio. You do not have permission to view this object.Īseptic technique improves patient safety and prevents healthcare-associated infections that may negatively impact outcomes including: increasing patient morbidity and mortality, increasing healthcare costs for patients and their families, prolonging length of stay, increasing resistance of microorganisms to antimicrobials, and increasing physical and mental discomfort for the patient.Ref 30-2 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Following observations of Ignaz Semmelweis and others over 100 years ago, the practice of aseptic technique is an infection prevention method that is recognized as an important factor in the prevention and transmission of healthcare-associated infections.Ref 30-1 Association of Perioperative Registered Nurses (AORN).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
